According to a survey issued from the partnership between the Arab Monetary Fund (AMF), the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, Arab banks are witnessing withdrawal of correspondent bank relationships (CBRs). As such, the survey aimed at identifying the causes and impacts of such changes.
The participating banks operated in 17 different countries of the Arab region, such as Algeria, Bahrain, Lebanon, Qatar… Of all the 216 banks surveyed, almost 40% witnessed significant declines in CBRs, 55% claimed no change, while 5% said they were improving. According to the survey, the US banks grasped the largest share of CBR withdrawals, followed by the UK, Germany, and KSA.
As for the main causes of these withdrawals, almost 42% of the surveyed banks claimed that the overall risk appetite of foreign financial institution was the driver behind this action, followed by “the legal and supervisory requirements in foreign financial institutions’ jurisdiction that have implications on maintaining CBRs”, such as the FATCA. Moreover, other identified drivers were the lack of profitability of certain CBR services/products, the sovereign credit risk rating of the respondent financial institutions’ national jurisdiction, and concerns about money laundering/terrorism financing risks in the respondent financial institutions’ national jurisdiction.
The withdrawal mostly impacted the trade finance and documentary collection services in the arab banks, followed by “money transfer operations and other remittance service providers.” Furthermore, the banks indicated that it has been costly to create new CBRs.
Breakdown of CBR Trend with Participant Banks
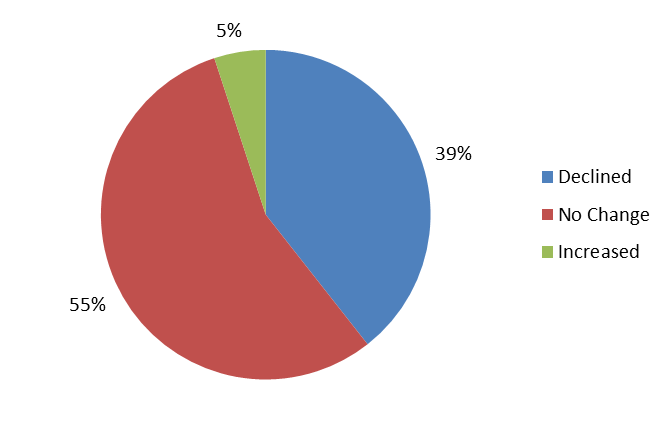
Source: IMF