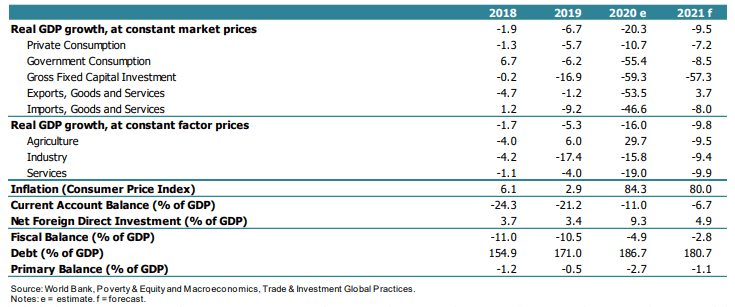
In its update on Lebanon, published in April 2021, the World Bank report estimates Lebanon’s Real GDP growth to contract by 20.3% in year 2020, in contrast to -6.7% in 2019. The estimated loss is a result of the financial, economic depression and the depreciating exchange rate which lost 50% of its value over March 12-16, 2021.
In fact, the banking sector had adopted informal capital control measures, mainly deleveraging on USD deposits settled prior to October 2019, thus not attracting depositors any longer. Overall, World bank explains the exchange rate depreciation along with surging inflation; World bank average exchange rate depreciated by 129% in 2020 and inflation increased to 84.3% from 2.9% in 2019; adding that the category of food and non-alcoholic beverages witnessed the highest portion, reading 254% in 2020.
It is important to mention that the prolonged distressed situation resulted in a social impact, which most likely will further deteriorate; moreover, the inflationary effect targeted vastly the poor making it harder to access food necessities and healthcare. The share of household facing deteriorating conditions reached 41% of the population, and difficulty in accessing health care increased to 36% of the household up from 25% in July-August 2020. In fact, majority of the labour force earn in the Lebanese lira local currency and are experiencing diminishing purchasing power and higher rates of unemployment.
It is worth mentioning that the PMI index measured an average of 41.4 in year 2020 below the threshold average of 50; mirroring the dwindling performance in the private sector activity such as drop in construction permits and freeze in capital inflows. Moreover, the breakdown also includes the decline in foreign exchange reserves at BDL dropping by $12.5 Billion yearly to reach $24.1 Billion by end of 2020. Furthermore, total revenue declined by 20.2% over the first eight months of 2020 as a result of the substantial reductions in telecom activity, VAT and customs revenues; subsequent to the Eurobond default in early March 2020 and to the interest payment cuts.
World bank’s further insights show a drop of 9.5% in real GDP in 2021 as political and economic stability remain out of reach. As important, a downgrade in income classification is foreseen to take place from an upper middle income economy of Gross National Income between $4,046 and $12,535 to a lower middle income economy, as income per-capita fell by 40% over the 2018-2020 period. As such, a restructuring framework is our only solution, and a recovery process to pick up the public finances and financial sector.