The rating agency Standard & Poor’s (S&P) maintained its rating on Lebanese pound bonds at SD for Foreign Currency and at CC for Long-Term Local Currency, with a negative long-term outlook.
S&P’s rationale for the ratings is partly due to Lebanon’s dysfunctional political environment and external security risks weigh on institutional effectiveness. S&P pointed out that following the Lebanese government’s default on its foreign currency obligations in March 2020, the fragmented political environment, limited legal capacity of the caretaker government to enact legislation, and delays in appointing key officials, including a new president and permanent BDL governor, slowed down the economic recovery process. Moreover, the Israel-Hamas war and the Israel-Hezbollah exchange of fire at the Lebanese southern borders increased Lebanon’s security risks.
Moreover, the RatingsDirect, issued on 19 August, 2024, pointed out that Lebanon has a very high stock of general government debt, weak balance of payments, and no monetary policy flexibility. Higher revenues from currency valuation changes, such as for customs taxes and airport fees, along with Lebanon’s spending constraints (due to its default) resulted in a small surplus (on a cash basis) for first-half 2024. But, resumption of foreign bilateral and multilateral concessional debt servicing and adjustment to the public sector salaries led to higher expenses than in 2023.
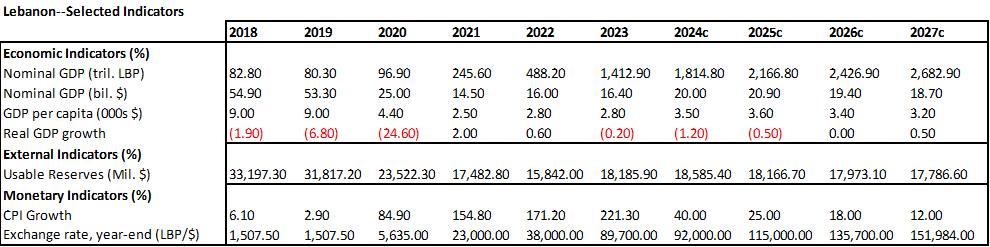
The RatingsDirect also made some interesting points:
Lastly, S&P declared that it would raise the foreign currency’s rating from SD, after the completion of the government’s commercial debt restructuring. As for the local currency’s negative outlook, S&P said that it is the result of the lack of restructuring for the local currency’s debt and the shortcomings in public sector administrative capacity.
S&P presented two scenarios for its future ratings. The rating agency would downgrade the local currency rating to SD in case of haircuts or maturity extensions on local currency debt, and in case the government missed local currency principal or interest payments to a commercial creditor. On the other hand, S&P would upgrade the outlook to stable or raise the local currency rating if domestic economic policymaking improved and the possibility of a distressed exchange of Lebanon’s local currency commercial debt has declined.
Disclaimer :
This article is a research document that is owned and published by Blominvest Bank SAL.
No material from this publication may be modified, copied, reproduced, repackaged, republished, circulated, transmitted or redistributed directly or indirectly, in whole or in any part, without the prior written authorization of Blominvest Bank SAL.
The information and opinions contained in this document have been compiled from or arrived at in good faith from sources deemed reliable. Neither Blominvest Bank SAL, nor any of its subsidiaries or affiliates or parent company will make any representation or warranty to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained herein.
Neither the information nor any opinion expressed in this research article constitutes an offer or a recommendation to buy or sell any assets or securities, or to provide investment advice.
This research article is prepared for general circulation and is circulated for general information only.